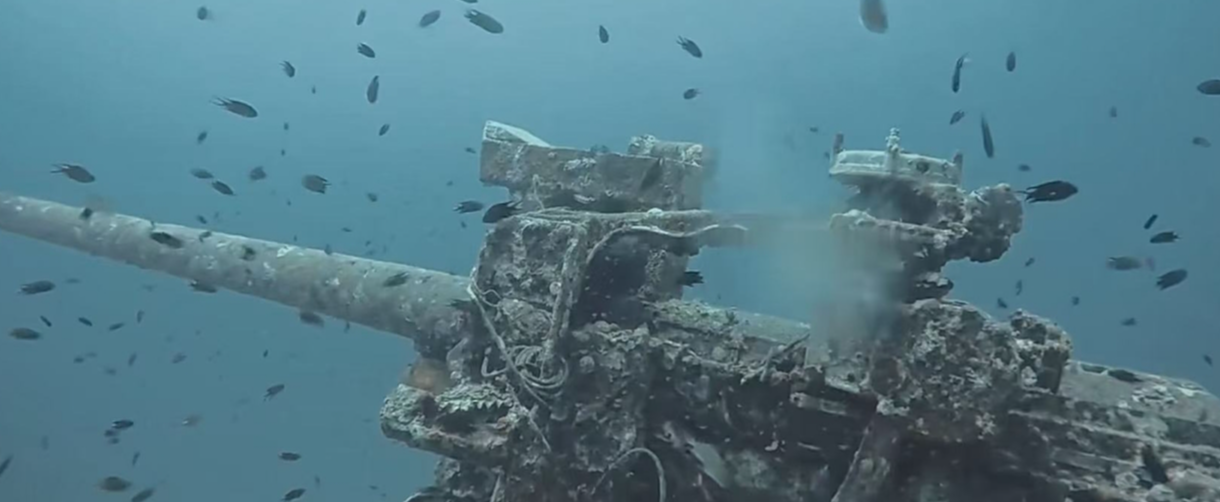
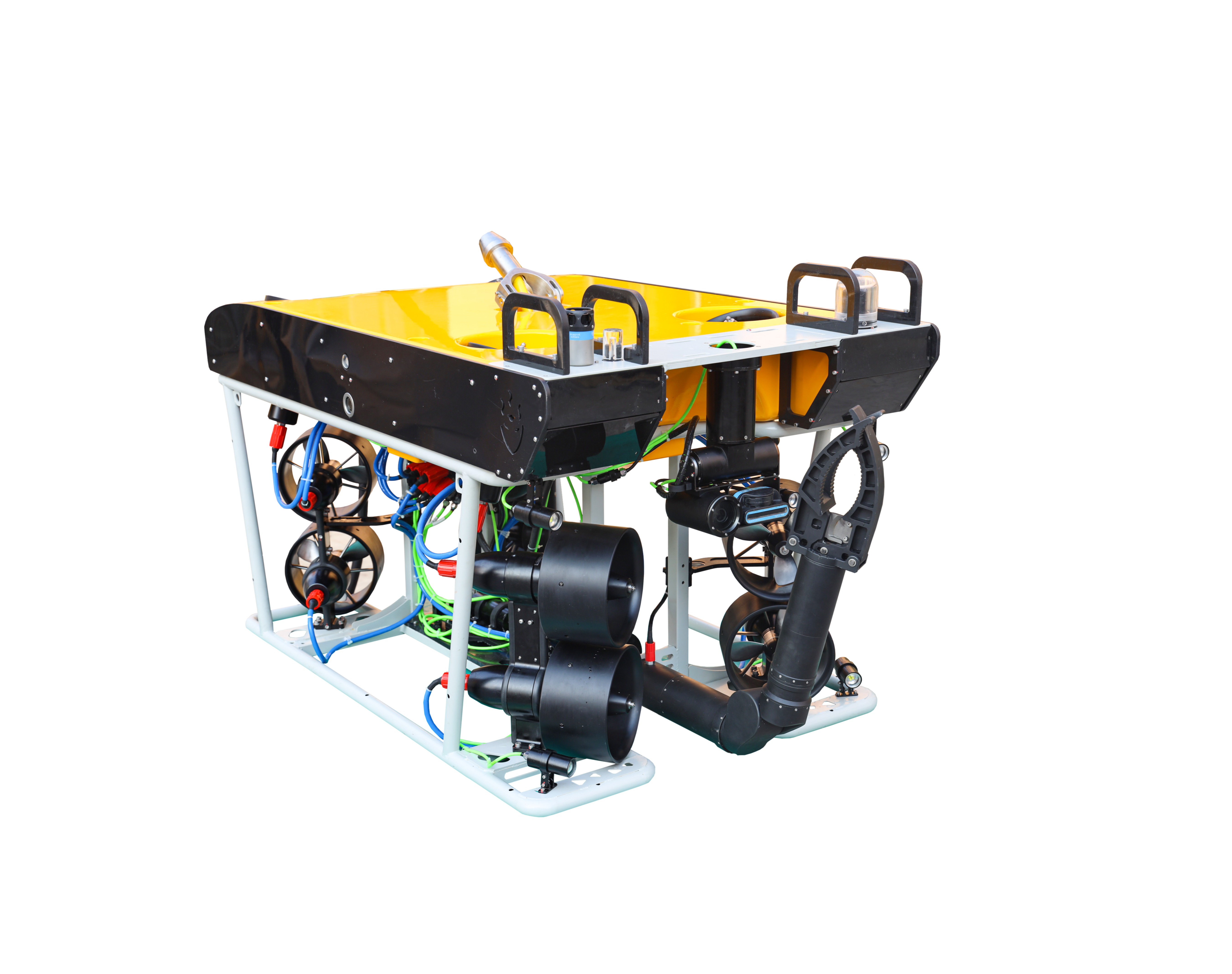
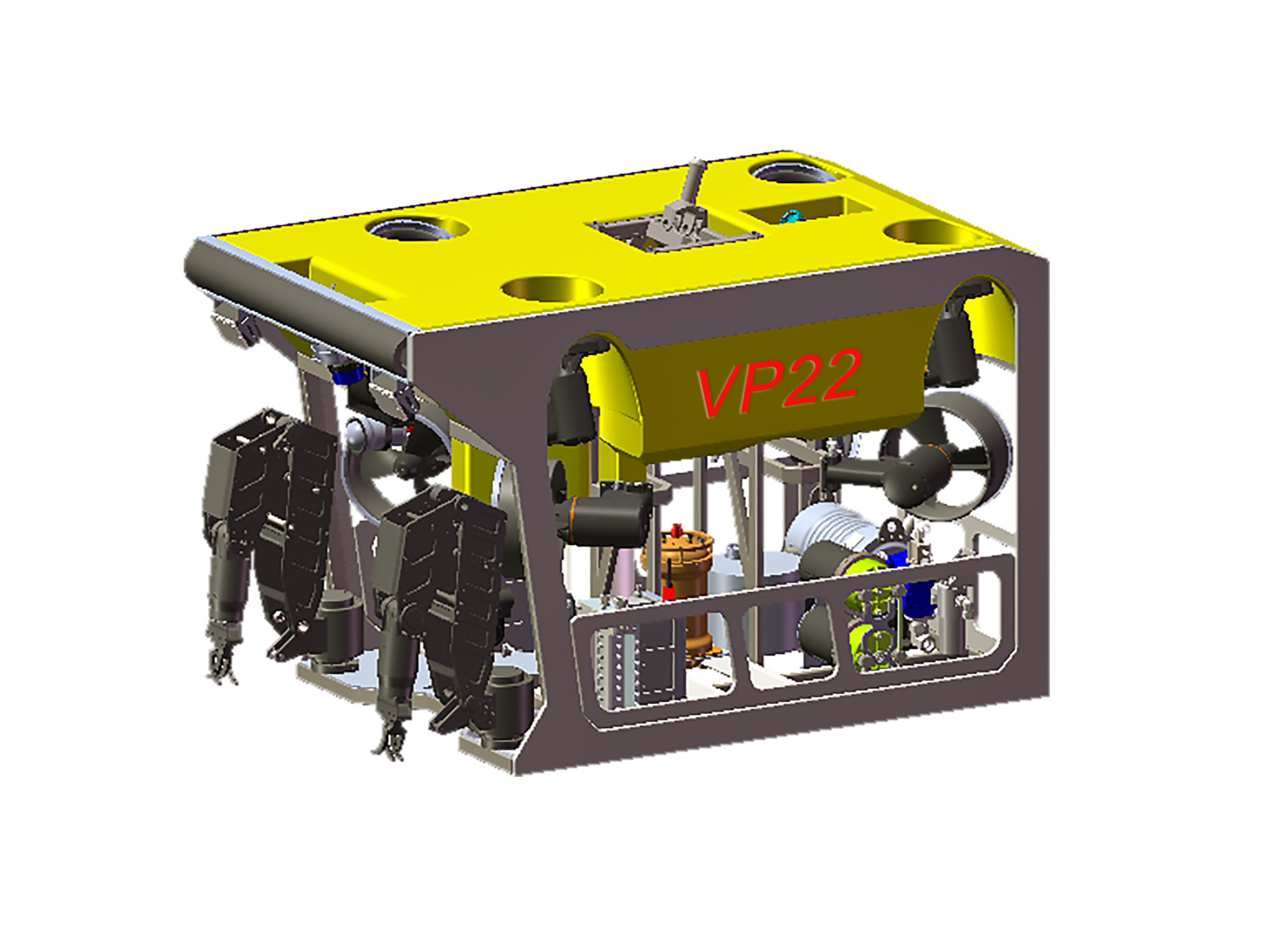
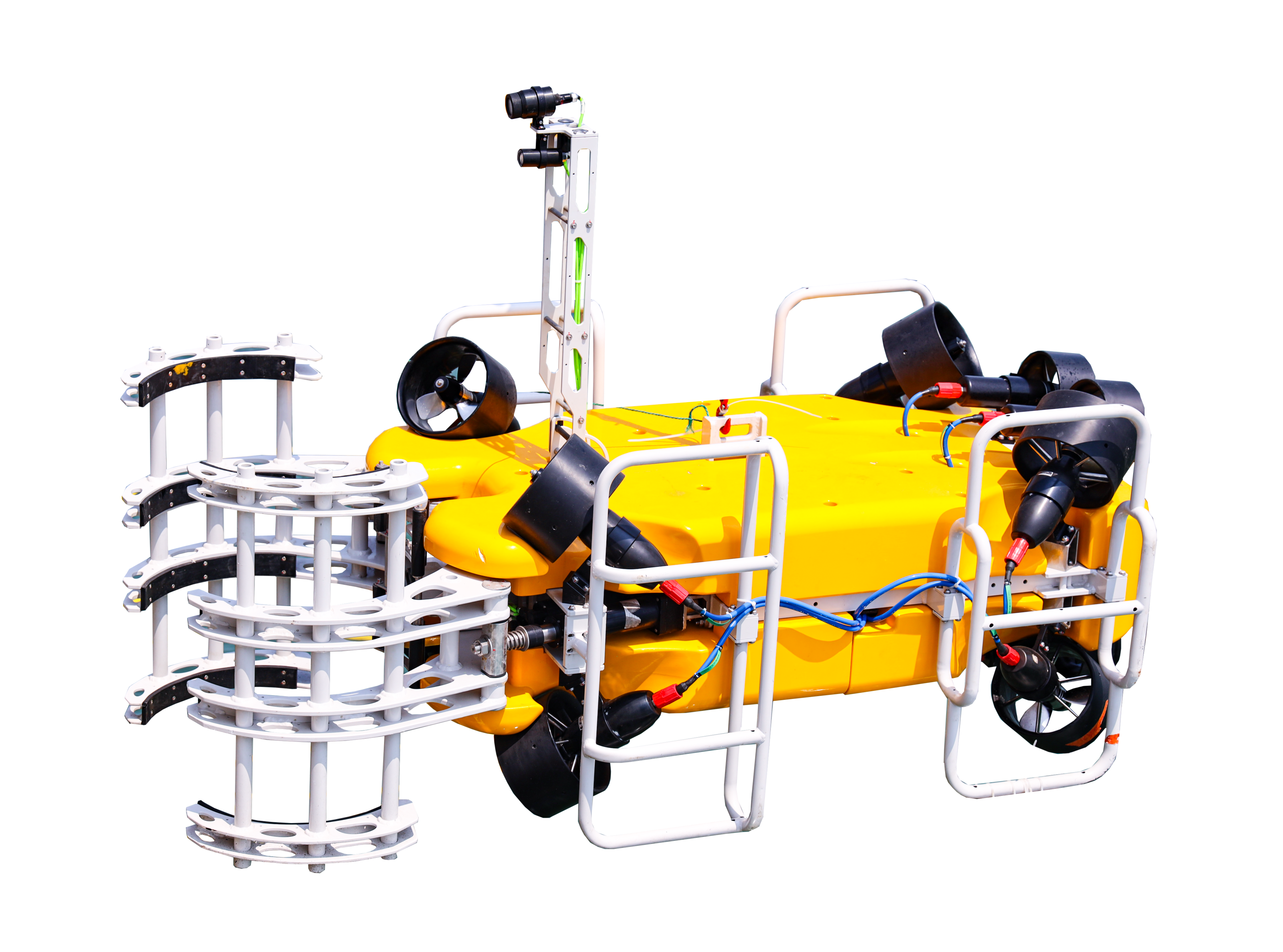
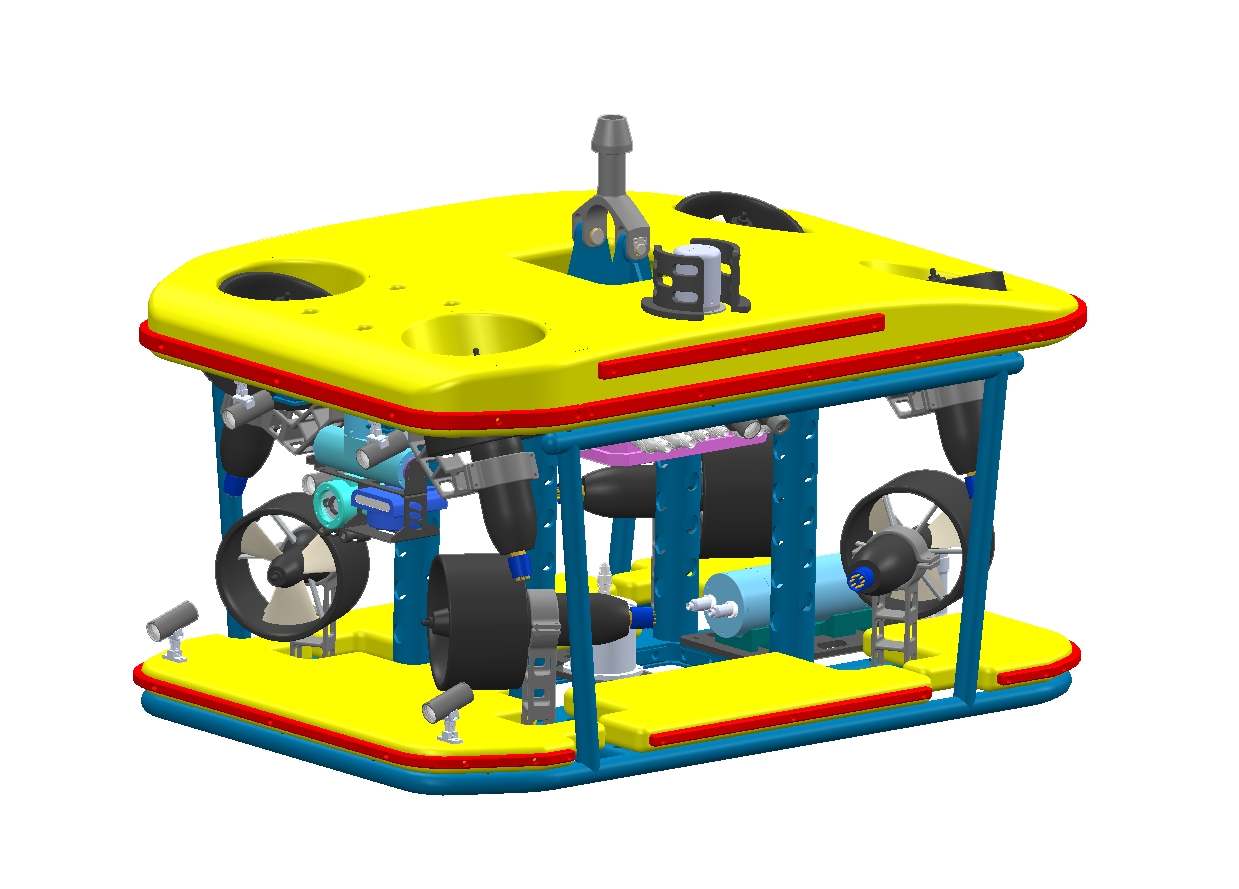
Underwater Salvage Overview & Application
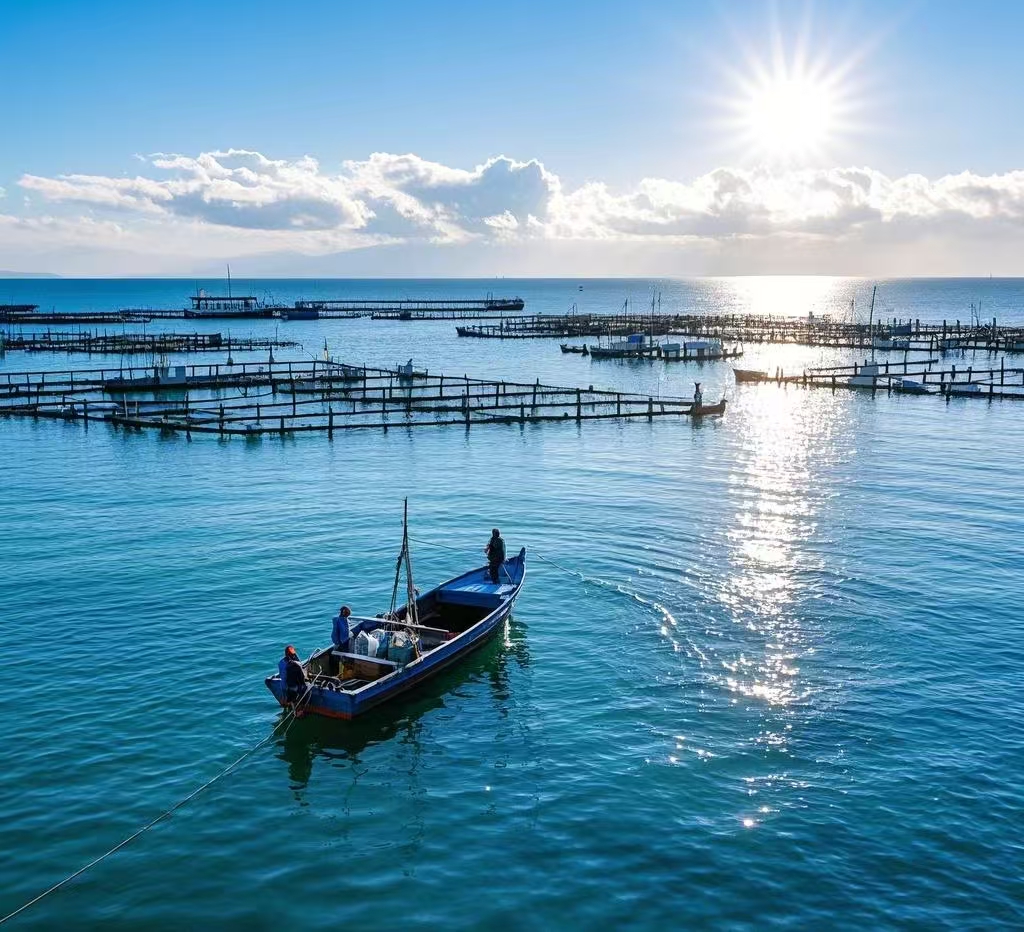
Underwater salvage is a complex underwater operation involving the recovery of objects or resources that have sunk to the seafloor, using advanced equipment and precise operations. The operating environments are typically deep seas, rivers, lakes, and other bodies of water, where working conditions are extremely harsh. The challenges of underwater salvage are primarily due to high pressure, low temperatures, strong currents, and poor visibility in deep water environments. Especially in deep-sea regions, the depth of operation and the complex underwater terrain impose high demands on the operation equipment and techniques. To effectively address these challenges, modern underwater salvage relies on high-performance remotely operated vehicles (ROVs), underwater robots, and intelligent control systems. These devices not only need to have efficient deep-sea operational capabilities but must also be able to operate stably in harsh environments, ensuring safety and reliability during the salvage process. With ongoing technological advancements, underwater salvage technology is evolving toward deeper water, higher efficiency, and greater intelligence.